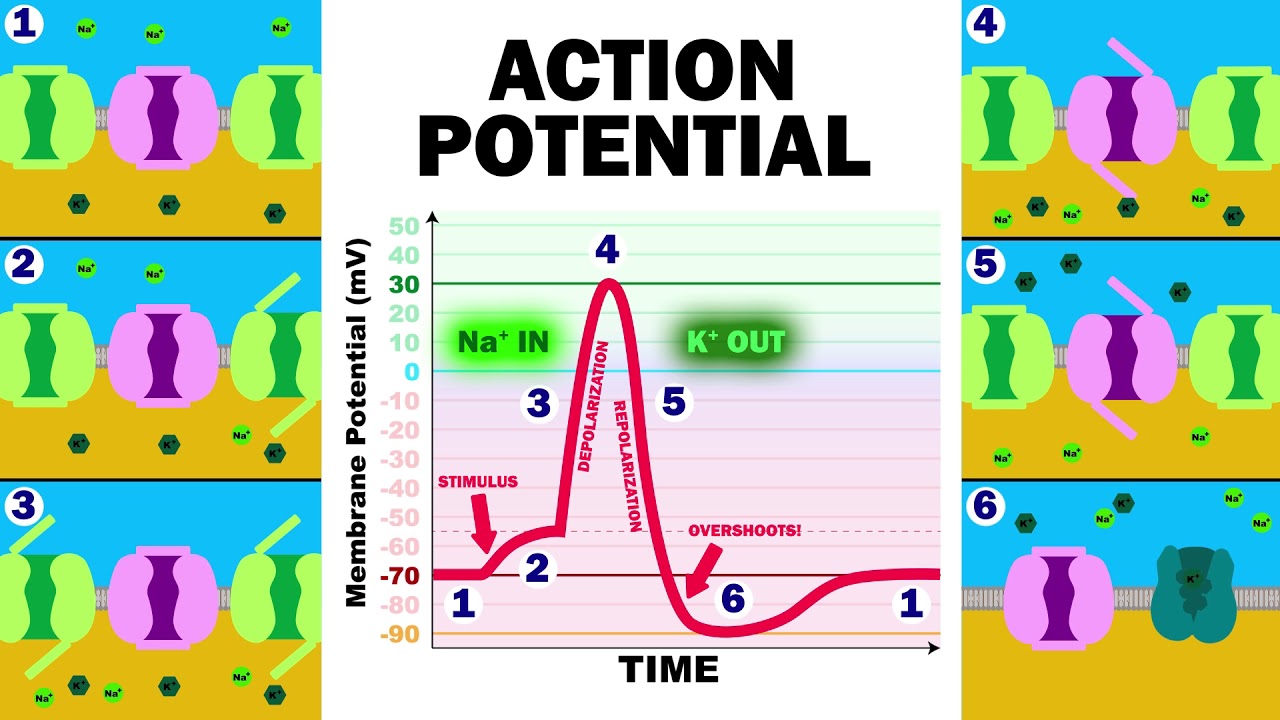
Ready to test your understanding of how neurons communicate? This quiz will take you through the intricate process of action potentials, from the initial stimulus to the transmission of nerve impulses. Sharpen your knowledge and see how well you understand this fundamental concept in neuroscience. Good luck!
We recommend that you do not leave the page that you are taking this quiz in. Stay honest 🙂
Action Potential Quiz Questions Overview
1. What is the resting membrane potential of a typical neuron?
-70 mV
-50 mV
0 mV
30 mV
2. Which ion is primarily responsible for the depolarization phase of an action potential?
Sodium (Na+)
Potassium (K+)
Calcium (Ca2+)
Chloride (Cl-)
3. What is the threshold potential that typically must be reached to trigger an action potential?
-55 mV
-70 mV
-90 mV
0 mV
4. Which phase of the action potential is characterized by the rapid influx of sodium ions?
Depolarization
Repolarization
Hyperpolarization
Resting phase
5. What causes the repolarization phase of an action potential?
Efflux of potassium ions (K+)
Influx of sodium ions (Na+)
Influx of calcium ions (Ca2+)
Efflux of chloride ions (Cl-)
6. Which ion channel is responsible for the initial depolarization of the neuron?
Voltage-gated sodium channels
Voltage-gated potassium channels
Ligand-gated chloride channels
Calcium channels
7. What is the refractory period in the context of an action potential?
A period when the neuron cannot fire another action potential
A period of increased sensitivity to stimuli
A period when the neuron is hyperpolarized
A period of rapid depolarization
8. What role do myelin sheaths play in action potential propagation?
They increase the speed of action potential propagation
They decrease the speed of action potential propagation
They prevent action potentials from occurring
They have no effect on action potential propagation
9. What is the function of the nodes of Ranvier in a myelinated neuron?
They allow for the rapid conduction of action potentials
They prevent the conduction of action potentials
They store neurotransmitters
They generate action potentials
10. During which phase do voltage-gated potassium channels open?
Repolarization
Depolarization
Resting phase
Threshold phase
11. What is the role of the sodium-potassium pump in maintaining the resting membrane potential?
It pumps sodium out of the cell and potassium into the cell
It pumps potassium out of the cell and sodium into the cell
It pumps calcium out of the cell
It pumps chloride into the cell
12. Which neurotransmitter is commonly released at the synapse following an action potential?
Acetylcholine
Dopamine
Serotonin
GABA
13. What is the term for the period during which a neuron is less likely to fire an action potential immediately after an action potential has occurred?
Relative refractory period
Absolute refractory period
Resting period
Depolarization period
14. What is the primary function of voltage-gated calcium channels in the presynaptic terminal?
They trigger the release of neurotransmitters
They generate action potentials
They maintain the resting membrane potential
They reuptake neurotransmitters
15. What is the all-or-none principle in the context of action potentials?
An action potential either occurs fully or not at all
An action potential can vary in strength
An action potential can be partially generated
An action potential depends on the strength of the stimulus
16. Which part of the neuron is primarily responsible for receiving incoming signals?
Dendrites
Axon
Cell body
Axon hillock
We recommend that you do not leave the page that you are taking this quiz in. Stay honest 🙂
Can Your Friends Do Better Than You in This Quiz?
Share this quiz with your friends and compare results.
Was this page helpful?
More Popular Biology Quizzes:
-
Leukocytes Identification Quiz
-
RNA and Protein Synthesis Quiz
-
Humerus Bone Quiz
-
Mutations Quiz
-
Protists and Fungi Quiz
-
Dihybrid Cross Quiz